Daylight Saving Time ends on 4 November 2018. 
Clocks will go back one hour on Sunday 4 November at 02:00. This means your devices will automatically reverse an hour at the strike of 2:00 a.m.,making it 1:00 a.m.
This information was obtained in an article entitled Daylight Saving Time 2018: A Guide to the When, Why, What and How (https://www.livescience.com/56048-daylight-saving-time-guide.html)
On Sunday, Nov. 4, most Americans will set their clocks back an hour, as daylight saving time (sometimes erroneously called daylight savings time) comes to a close, and most of the United States will “lose” an hour of daylight. These spring and fall clock changes continue a long tradition started by Benjamin Franklin to conserve energy. (This year, however, the Sunshine State is aiming to stop the change and remain in DST year-round, according to a Senate bill and news reports.)
Below is a look at when daylight saving time starts and ends during the year, its history, why we have it now and some myths and interesting facts about the time change.
How Did It Start? 
Benjamin Franklin takes the honor (or the blame, depending on your view of the time changes) for coming up with the idea to reset clocks in the summer months as a way to conserve energy, according to David Prerau, author of “Seize the Daylight: The Curious and Contentious Story of Daylight Saving Time” (Thunder’s Mouth Press, 2005). By moving clocks forward, people could take advantage of the extra evening daylight rather than wasting energy on lighting. At the time, Franklin was ambassador to Paris and so wrote a witty letter to the Journal of Paris in 1784, rejoicing over his “discovery” that the sun provides light as soon as it rises.
Even so, DST didn’t officially begin until more than a century later. Germany established DST in May 1916 as a way to conserve fuel during World War I. The rest of Europe came onboard shortly thereafter. And in 1918, the United States adopted daylight saving time.
Though President Woodrow Wilson wanted to keep daylight saving time after WWI ended, the country was mostly rural at the time and farmers objected, partly because it would mean they lost an hour of morning light. (It’s a myth that DST was instituted to help farmers.) And so daylight daylight saving time was abolished until the next war brought it back into vogue. At the start of WWII, on Feb. 9, 1942, President Franklin Roosevelt re-established daylight saving time year-round, calling it “War Time.” [Learn more about the crazy history of Daylight Saving Time]
After the war, a free-for-all system in which U.S. states and towns were given the choice of whether or not to observe DST led to chaos. And in 1966, to tame such “Wild West” mayhem, Congress enacted the Uniform Time Act. That federal law meant that any state observing DST — and they didn’t have to jump on the DST bandwagon — had to follow a uniform protocol throughout the state in which daylight saving time would begin on the first Sunday of April and end on the last Sunday of October.
Then, in 2007, the Energy Policy Act of 2005 went into effect, expanding the length of daylight saving time to the present timing.
Why do we still have daylight saving time?
Fewer than 40 percent of the world’s countries observe daylight saving time, according to timeanddate.com. However, those who do take advantage of the natural daylight in the evenings. That’s because the days start to get longer as Earth moves from the winter season to spring and summer, with the longest day of the year on the summer solstice. During the summer, Earth, which revolves around its axis at an angle, is tilted directly toward the sun (at least its top half).
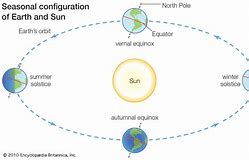
As Earth orbits the sun, it also spins around its own imaginary axis. Because it revolves around this axis at an angle, different parts of our planet experience the sun’s direct rays at different times of the year, leading to the seasons.
Credit: BlueRingMedia / Shutterstock.com
Regions farthest away from the equator and closer to the poles get the most benefit from the DST clock change, because there is a more dramatic change in sunlight throughout the seasons.
Research has also suggested that with more daylight in the evenings, there are fewer traffic accidents, as there are fewer cars on the road when it’s dark outside. More daylight also could mean more outdoor exercise (or exercise at all) for full-time workers.
Energy savings
The nominal reason for daylight saving time has long been to save energy. The time change was first instituted in the United States during World War I, and then reinstituted again during World War II, as a part of the war effort. During the Arab oil embargo, when Arab members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) stopped selling petroleum to the United States, Congress even enacted a trial period of year-round daylight saving time in an attempt to save energy.
But the evidence for energy savings is slim. Brighter evenings may save on electric lighting, said Stanton Hadley, a senior researcher at Oak Ridge National Laboratory who helped prepare a report to Congress on extended daylight saving time in 2007. But lights have become increasingly efficient, Hadley said, so lighting is responsible for a smaller chunk of total energy consumption than it was a few decades ago. Heating and cooling probably matter more, and some places may need air-conditioning for the longer, hotter evenings of summer daylight saving time.
Hadley and his colleagues found that the four weeks of extra daylight saving time that went into effect in the United States in 2007 did save some energy, about half of a percent of what would have otherwise been used on each of those days. However, Hadley said, the effect of the entire months-long stretch of daylight saving could very well have the opposite effect. A 1998 study in Indiana before and after implementation of daylight saving time in some counties found a small increase in residential energy usage. Temporary changes in Australia’s daylight saving timing for the summer Olympics of 2000 also failed to save any energy, a 2007 study found.
Part of the trouble with estimating the effect of daylight saving time on energy consumption is that there are so few changes to the policy, making before-and-after comparisons tricky, Hadley told Live Science. The 2007 extension of daylight saving time allowed for a before-and-after comparison of only a few weeks’ time. The changes in Indiana and Australia were geographically limited.
Ultimately, Hadley said, the energy question probably isn’t the real reason the United States sticks with daylight saving time, anyway.
“In the vast scheme of things, the energy saving is not the big driver,” he said. “It’s people wanting to take advantage of that light time in the evening.”
Who observes daylight saving time? (and who doesn’t)
Most of the United States and Canada observe DST on the same dates. But of course, there are exceptions. Hawaii and Arizona are the two U.S. states that don’t observe daylight saving time, though Navajo Nation, in northeastern Arizona, does follow DST, according to NASA.
And, every year there are bills put forth to get rid of DST in various states, as not everyone is keen on turning their clocks forward an hour. This year, Florida’s Senate and House passed legislation called the Sunshine Protection Act that would ask the U.S. Congress to exempt the state from the federal 1966 Uniform Time Act. If approved, Florida would remain in DST year-round. In order to allow Florida’s year-round DST, however, the U.S. Congress would have to amend the Uniform Time Act (15 U.S.C. s. 260a) to authorize states this allowance, according to The New York Times.
And in California, voters may get to decide: In this fall’s statewide ballot, voters can vote for or against Proposition 7 that would attempt to repeal the annual clock changes. If the Prop gets approved, that would mean the Legislature can act to eliminate the time changes, possibly leading to year-round DST, according to Land Line magazine.
Other states have also proposed exemptions from the federal time act. For instance, Sen. Ryan Osmundson, R-Buffalo, introduced Senate Bill 206 into the Senate State Administration Committee in February 2017, which would exempt Montana from daylight saving time, keeping the state on standard time year-round, according to the bill. Three bills put forth last year in Texas aimed to abolish DST for good: House Bill 2400, Senate Bill 238 and House Bill 95, according to the broadcast company kxan. Nebraskans may be off the hook for clock changes as well. In January 2017, state Sen. Lydia Brasch, a Republican of Bancroft, proposed a bill called LB309 to eliminate daylight saving time in the state, according to the bill.
Some regions of British Columbia and Saskatchewan don’t change their clocks. These include the following areas in British Columbia: Charlie Lake, Creston (East Kootenays), Dawson Creek, Fort St. John, and Taylor; In Saskatchewan, only Creighton and Denare Beach observe DST, according to NASA.
Most of Europe currently observes daylight saving time, called “summer time,” which begins at 1 a.m. GMT on the last Sunday in March and ends (winter time) at 1 a.m. GMT on the last Sunday in October. However, even the European Union may propose an end to clock changes, as a recent poll found that 84 percent of 4.6 million people surveyed said they wanted to nix them, the Wall Street Journal reported.
If the lawmakers and member states agree, the EU members could decide to keep the EU in summer time or winter time, according to the WSJ.
The United Kingdom moved their clocks forward on March 26, 2017, and back again to standard time on Oct. 29, 2017, according to the U.K. government. They performed this same ritual on March 25, and will again on Oct. 28, 2018.
The DST-observing countries in the Southern Hemisphere — in Australia, New Zealand, South America and southern Africa — set their clocks an hour forward sometime during September through November and move them back to standard time during the March-April timeframe.
Australia, being such a big country (the sixth-largest in the world), doesn’t follow DST uniformly: New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, Tasmania and the Australian Capital Territory follow daylight saving, while Queensland, the Northern Territory (Western Australia) do not, according to the Australian government. Clocks in the observing areas spring forward an hour at 2 a.m. local time on the first Sunday in October and push back an hour at 3 a.m. local daylight time on the first Sunday in April.
Russia instituted year-round daylight saving time in 2011, or permanent “summer time,” which seemed dandy at first. But in the depths of winter, sunrise occurred at 10 a.m. in Moscow and 11 a.m. in St. Petersburg, Prerau, author of “Seize the Daylight: The Curious and Contentious Story of Daylight Saving Time,” said. This meant Russians had to start their days in the cold, pitch-dark. The permanent summer is coming to an end, however, as now Russian president Vladimir Putin abolished DST in 2014, according to BBC News. As such, the country will remain in “winter time” forever, or until another law is passed.
Myths and Interesting Facts
- Turns out, people tend to have more heart attackson the Monday following the “spring forward” switch to daylight saving time. Researchers reporting in 2014 in the journal Open Heart, found that heart attacks increased 24 percent on that Monday, compared with the daily average number for the weeks surrounding the start of DST.
- Before the Uniform Time Act was passed in the United States, there was a period in which anyplace could or could not observe DST, leading to chaos. For instance, if one took a 35-mile bus ride from Moundsville, West Virginia, to Steubenville, Ohio, he or she would pass through no fewer than seven time changes, according to Prerau. At some point, Minneapolis and St. Paul were on different clocks.
- A study published in 2009 in the Journal of Applied Psychologyshowed that during the week following the “spring forward” into DST, mine workers got 40 minutes less sleepand had 5.7 percent more workplace injuries than they did during any other days of the year.
- Pets notice the time change, as well. Since humans set the routines for their fluffy loved ones, dogs and cats living indoors and even cows are disrupted when, say, you bring their food an hour late or come to milk them later than usual, according to Alison Holdhus-Small, a research assistant at CSIRO Livestock Industries, an Australia-based research and development organization.
- The fact that the time changes at 2 a.m. at least in the U.S., may have to do with practicality. For instance, it’s late enough that most people are home from outings and setting the clock back an hour won’t switch the date to “yesterday.” In addition, it’s early enough not to affect early shift workers and early churchgoers.
Editor’s Note: This article was first published on Sept. 9, 2016, and then updated by Stephanie Pappas with information about energy use during daylight saving time. It was also updated in March 2017 to include bills put forth in the United States to eliminate DST in certain states, and again in 2018.








